- University of Lodz
- Faculty of Chemistry
- Department of Environmental Chemistry
- Scientific projects
Scientific projects
It is commonly known that pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) and cysteine (Cys) are present in human biofluids. It is also widely agreed that they are linked to some diseases. Moreover, PLP has been shown to undergo facile condensation with Cys under physiological conditions leading to 2-pyridoxyl-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (PTCA). Since PLP and Cys are ubiquitous in humans one can reasonably state that PTCA can be present in living organisms. Verification of this thesis is the main goal of the project. An additional aims are centered around the synthesis and purification of PTCA, confirmation of its chemical structure and testing the stability, elaboration of a new, precise and accurate chromatography based methods for the determination of PTCA in biological fluids.
Duration time: 19.07.2018 – 18.01.2023
Principal Investigator: prof. dr hab. Rafał Głowacki
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Lodz
Some important publications:
- J. Piechocka, M. Wrońska, R. Głowacki, Chromatographic strategies for the determination of aminothiols in human saliva, Trends Anal. Chem – TrAC, 126 (2020) 115866
- J. Piechocka, M. Wrońska, I.E. Głowacka, R. Głowacki, 2-(3-Hydroxy-5-phosphonooxymethyl-2-methyl-4-pyridyl)-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid, Novel Metabolite of Pyridoxal 5’-Phosphate and Cysteine Is Present in Human Plasma - Chromatographic Investigations, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (2020) 3548
- P. Kubalczyk K. Purgat, P. Olejarz, I. Kośka, R. Głowacki, Determination of homocysteine thiolactone in human urine by capillary zone electrophoresis and single drop microextraction, Anal. Biochem., 596 (2020) 113640
- J. Piechocka, M. Wrońska, G. Chwatko, H. Jakubowski, R. Głowacki, Quantification of homocysteine thiolactone in human saliva and urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. B. 1149 (2020) 122155
- J. Piechocka, M. Wieczorek, R. Głowacki, Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry Based Approach For the Determination of Methionine – Related Sulfur Containing Compounds In Human Saliva, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 2020, 9252
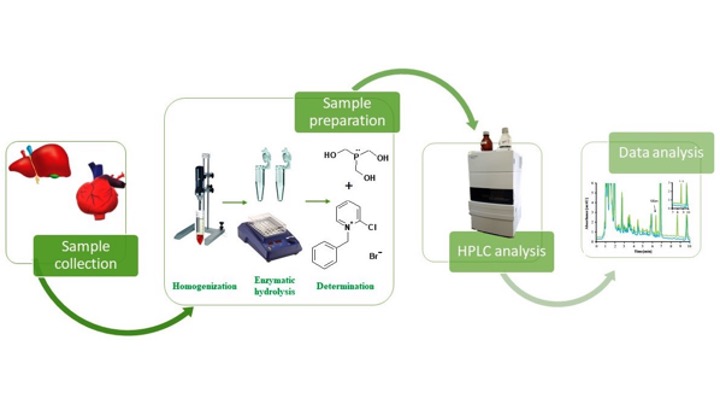
Duration time: 05.10.2017 – 04.04.2021
Principal Investigator: mgr Adrianna Kinga Kamińska
Scientific Supervisor: dr hab. Grażyna Chwatko, prof. UŁ
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
Lipoic acid (LA). is an universal antioxidant and metal chelator. LA prevents a number of age-related diseases and alleviates its negative effects. It is also used as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and neurovascular abnormalities associated with diabetic neuropathy. LA is readily absorbed from the diet and incorporated into other tissues through the blood stream mostly in the form of lipoyllysine. The research project is focused on the development of methods for the simultaneous determination of lipoic acid and lipoyllysine in foodstuffs, to examine the influence of food processing and food additives on the content of LA and lipoyllysine in consumed products, as well as to determine antioxidant capacity of lipoyllysine in a form of chemical compound and as a food component. These studies carried out during the project will provide the key information about the bioavailability of LA and lipoyllysine.
The most important publications:
- Kamińska A., Chwatko G., Estimation of lipoyllysine content in meat and its antioxidative capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68 (2020) 10992-10999. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03778
- Kamińska A., Głowacka I.E., Pasternak B., Głowacki R., Chwatko G., The first method for determination of lipoyllysine in human urine after oral lipoic acid supplementation. Bioanalysis 11 (2019) 1359-1373. https://www.future-science.com/doi/abs/10.4155/bio-2019-0011
Duration time: 10.2018 - 10.2019 (12 months)
Principal Investigator: dr Justyna Piechocka
Project Contractor: dr Justyna Piechocka
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
The most important publications:
-
Justyna Piechocka, Monika Wrońska, Grażyna Chwatko, Hieronim Jakubowski, Rafał Głowacki, Quantification of homocysteine thiolactone in human saliva and urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, Journal of Chromatography B, 1149 (2020) 122155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122155
-
Justyna Piechocka, Monika Wrońska, Rafał Głowacki, Chromatographic strategies for the determination of aminothiols in human saliva, Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 126 (2020) 115866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115866
The implementation of the project enabled us to verify the thesis concerning the possibility of the formation of derivatives in the body which are reactions products of aldehydes with some endogenous sulfur compounds. In the first phase of the project, the reactivity of formic, acetic aldehydes and PLP towards Hcy and Cys was confirmed. However, it was just as important to show that N-Hcy-albumin and Nε-Hcy-Lys undergo a similar reaction. An another important achievement concerns the use of PLP for the determination of Cys and Hcy in human plasma in the form of their thiazolidine and thiazine derivatives.
Duration time: 2013-07-19 – 2016-01-18
Principal Investigator: prof. dr hab. Rafał Głowacki
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Lodz
Some important publications:
- R. Głowacki, J. Stachniuk, K. Borowczyk, H. Jakubowski, Quantification of homocysteine and cysteine by derivatization with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 408 (2016) 1935–1941
- K. Borowczyk, M. Wyszczelska-Rokiel, P. Kubalczyk, R. Głowacki, Simultaneous determination of albumin and low-molecular-mass thiols in plasma by HPLC with UV detection, J. Chromatogr. B, 981–982 (2015) 57–64
- P. Furmaniak, P. Kubalczyk, R. Głowacki, Determination of homocysteine thiolactone in urine by field amplified sample injection and sweeping MEKC method with UV detection, J. Chromatogr. B, 961 (2014) 36–41
The most important goal of the project was to develop a new, sensitive and accurate method for the determination of the proteolytic degradation product of N-homocysteinylated proteins, namely Nε-Hcy-Lys.
Duration time: 2011-12-13 – 2013-06-12
Principal Investigator: dr Kamila Borowczyk
Scientific Supervisor: prof. dr hab. Rafał Głowacki
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Lodz
Some important publications:
- R. Głowacki, K. Borowczyk, E. Bald, Determination of Nε-homocysteinyllysine and g-glutamylcysteine in plasma by liquid chromatography with UV detection, J. Anal. Chem., 69 (2014) 645-651.
Duration time: 04.2021 - 04.2023 (24 months)
Principal Investigator: dr Justyna Piechocka
Project Contractor: dr Justyna Piechocka
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
The most important publications:
-
J. Piechocka, N. Litwicka, R. Głowacki, Identification and determination of 1,3-thiazinane-4-carboxylic acid in human urine - chromatographic studies, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (2022) 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020598
Duration time: 05.2022 - 05.2023 (12 months)
Principal Investigator: dr hab. Paweł Kubalczyk, prof. UŁ
Project Conctractor: mgr Izabella Kośka, dr hab. Paweł Kubalczyk, prof. UŁ
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
Modern, intensive methods of animal husbandry cause high demand for veterinary drugs, including antibiotics. It seems that nowadays animal production is almost impossible without the use of antibiotics. Since their discovery, these substances have been widely used in veterinary medicine, both for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. Apart from the therapeutic effect, i.e. the improvement of the animal health condition, the antibiotics added to the feed stimulate the growth and production benefits. Wrong utilization or abuse of antibacterial substances in breeding and agriculture, and also in human and veterinary medicine, at the same time contributed to the emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms with increasingly more efficient mechanisms of resistance on a broad scale. The aim of our project is to develop a new, precise and accurate capillary electrophoresis method for the determination of some fluoroquinolones. The implementation of these studies will provide new, fast and efficient tools, and these studies can be used for the routine analysis of animal tissues for the content of certain veterinary drugs.
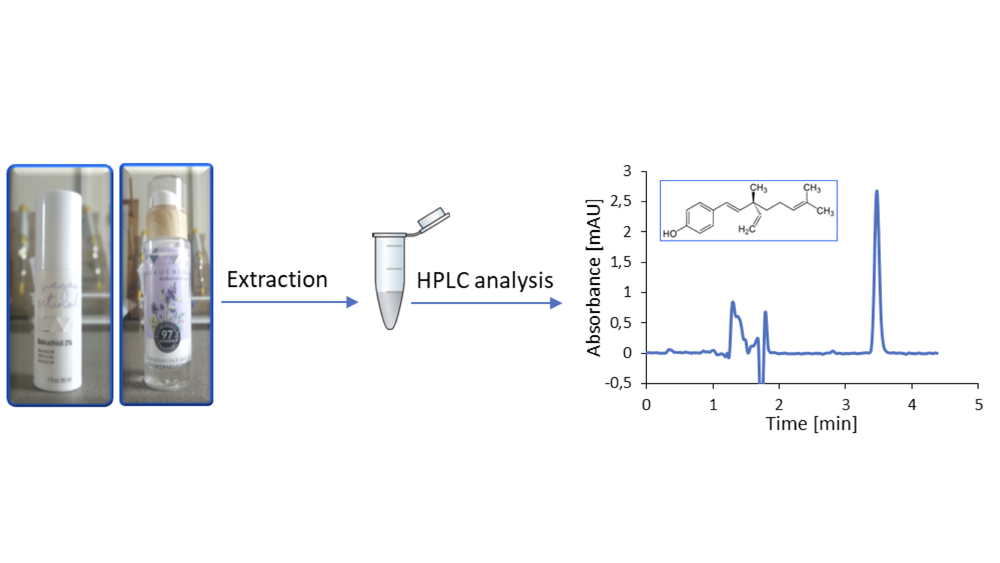 Duration time: 01.02.2022 – 31.01.2023
Duration time: 01.02.2022 – 31.01.2023
Principal Investigator: dr hab. Grażyna Chwatko, prof. UŁ
Project Contractor: mgr Katarzyna Kurpet, dr hab. Grażyna Chwatko, prof. UŁ,
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
Bakuchiol is a chemical compound found in plants widespread in Asia (Psoralea corylifolia L.). Bakuchiol is widely used in cosmetology and dermatology, due to its antioxidant, antimicrobial, emulsifying, and skin-improving properties. Concomitantly its similar action to retinol, it is called "plant retinol" or "vegan retinol". On cosmetic blogs, it was described as the discovery of the autumn-winter 2020 cosmetic season. Despite the wide interest in this compound, there is little information about possible changes that bakuchiol undergoes in cosmetics, and no analytical methods are enabling its determination in beauty products. Therefore, the project aims (a) to develop new, sensitive, selective, and fast methods of chromatographic determination of bakuchiol in cosmetics, (b) to use the obtained methods to determine the short- and long-term stability of bakuchiol in cosmetics, and (c) check whether bakuchiol will remain unchanged in preparations stored under various conditions.
Duration time: 12.2021 – 12.2023 (24 months)
Principal Investigator: mgr Katarzyna Kurpet
Project Contractor: mgr Katarzyna Kurpet
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
Numerous reports demonstrating the relationship between thrombosis and coronavirus infection and COVID-19 vaccination, as well as recent evidence suggesting the influence of homocysteine on platelet reactivity, and thus its role as a risk factor for thromboembolism, constitute important premises for undertaking research to assess the predictive value of homocysteine and its metabolites as specific markers of the development of cardiovascular diseases.
The main objective of the project is to evaluate the impact of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection and COVID-19 vaccination on the development of hyperhomocysteinemia of varying severity in convalescents and vaccinated subjects within twelve months of the initiation of the body’s immune response. The research experiment will be based on measuring the concentration of various forms of homocysteine and related to it in the metabolic pathway of low-molecular-weight thiols, such as cysteine, glutathione, γ-glutamylcysteine, and cysteinylglycine in plasma samples collected four weeks, three, six, and twelve months after the second dose of vaccine or recovery, respectively. The determinations will be carried out with the use of chromatographic methods developed and validated at the Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz. In addition, whole blood counts will be performed at the same time intervals to investigate the effect of homocysteine on thrombocyte reactivity.
The expected results may contribute to broadening the understanding of the potential mechanisms of COVID-19-related thrombosis, as well as determining the usefulness of biothiols as early long-term biomarkers of adverse cardiovascular side effects after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 disease. The information obtained during the planned research experiment may provide a basis for future studies on large populations.
Duration time: 02.2023 – 08.2023 (7 months)
Principal Investigator: mgr Izabella Kośka
Project Contractor: mgr Izabella Kośka
Place of implementation: Department of Environmental Chemistry, University of Lodz
Among the drugs administered to animals are tranquilizers, which are mainly administered to pigs during transport to the slaughterhouse to minimize the risk of animal death and maintain high meat quality. Due to the widespread use of these compounds, drug residues are sometimes present in food. The administration of veterinary drugs should be discontinued for an appropriate period of time before the slaughter of animals, because consuming meat in which drug residues are present is dangerous to the health of consumers.
For this reason, it is very important to determination of veterinary drug residues in food, and since continuous monitoring is essential, laboratories are forced to develop sensitive and reliable methods for determining these compounds. In view of the above, the main goal of the project is to develop a new, precise and accurate chromatographic method for the determination of some sedative drugs (azaperone and its metabolite azaperol). The implementation of the project will provide fast and efficient tools that can be successfully used for routine analysis of animal tissues for the content of the veterinary drugs.
